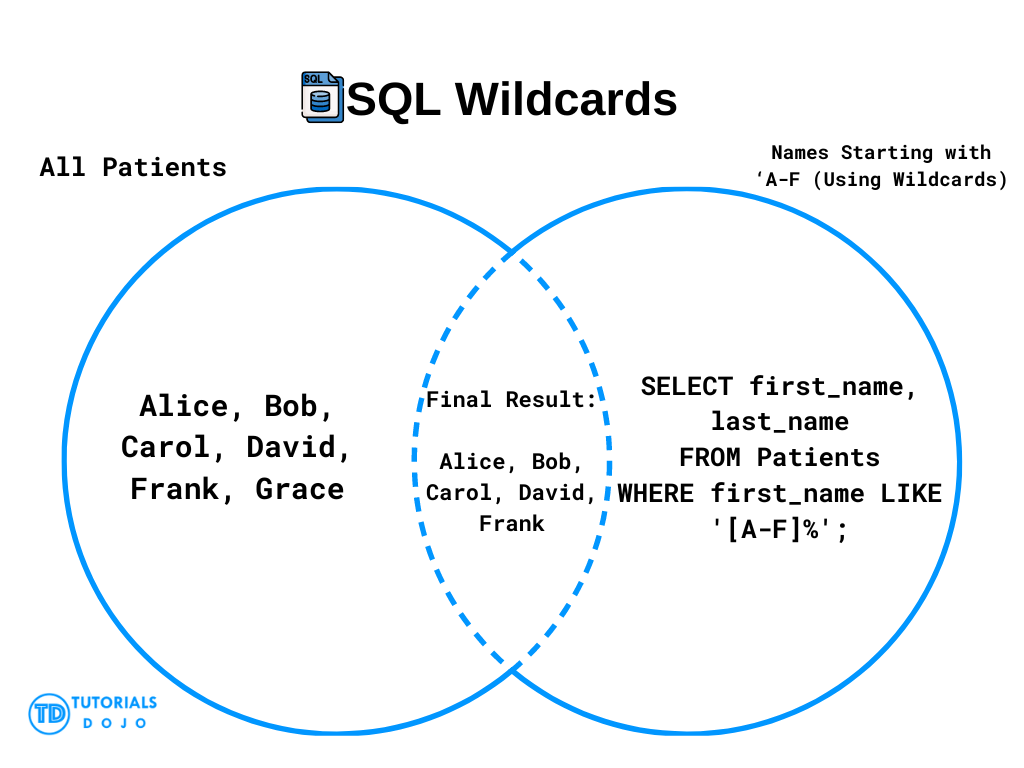
The SQL Wildcards are used in the LIKE operator to search for a specified pattern in a column. Wildcards allows you to filter results based on partial matches rather than exact values, making it easier to find relevant data in large databases.
SQL Wildcard Syntax
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name WHERE column_name LIKE pattern;
SQL Wildcard Characters
- % : Represents zero or more characters.
- _ : Represents a single character.
- [] : Represents any single character within the brackets.
- – : Used within brackets to specify a range of characters.
- ^: Represents ay character not in the brackets.
SQL Wildcard Microsoft Access Wildcard
- * : Used instead of % to represent zero or more characters.
- ? : Used instead of _ to represent a single character.
Note: These are specific to Microsoft Access databases, so in those environments, you would use * and ? instead of & and _.
SQL Wildcard Example
SQL Wildcard Using The % Wildcard Example
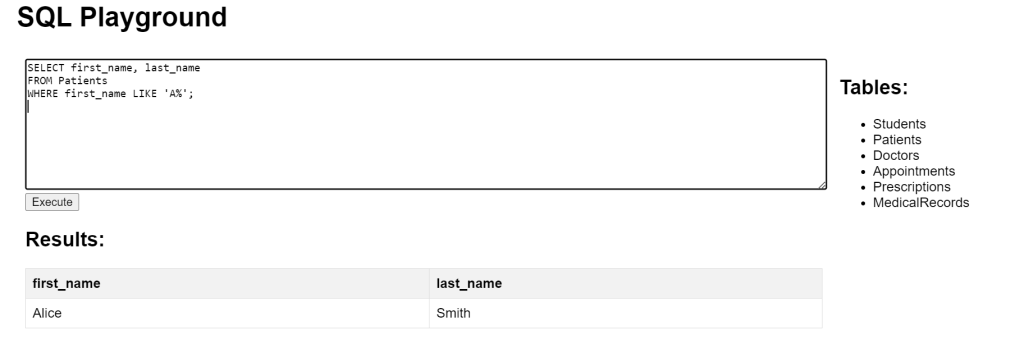
This query uses the % wildcard to find all patients whose first names starts with letter ‘A’.
SELECT first_name, last_name FROM Patients WHERE first_name LIKE 'A%';
SQL Wildcard Visual Diagram