In SQL, ANY and ALL are operators used to compare a value with a set of values returned by a subquery. They enable more flexible filtering of query results by comparing the main query’s value with the values produced by the subquery.
SQL Any and All Syntax
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name WHERE column_name comparison_operator ANY (subquery); SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name WHERE column_name comparison_operator ALL (subquery);
SQL All With Select Syntax
SELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE column_name comparison_operator ALL (SELECT column_name FROM another_table);
SQL All With WHERE and HAVING Syntax
SELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE column_name > ALL (SELECT column_name FROM another_table); SELECT column_name, COUNT(*) FROM table_name GROUP BY column_name HAVING COUNT(*) > ALL (SELECT COUNT(*) FROM another_table);
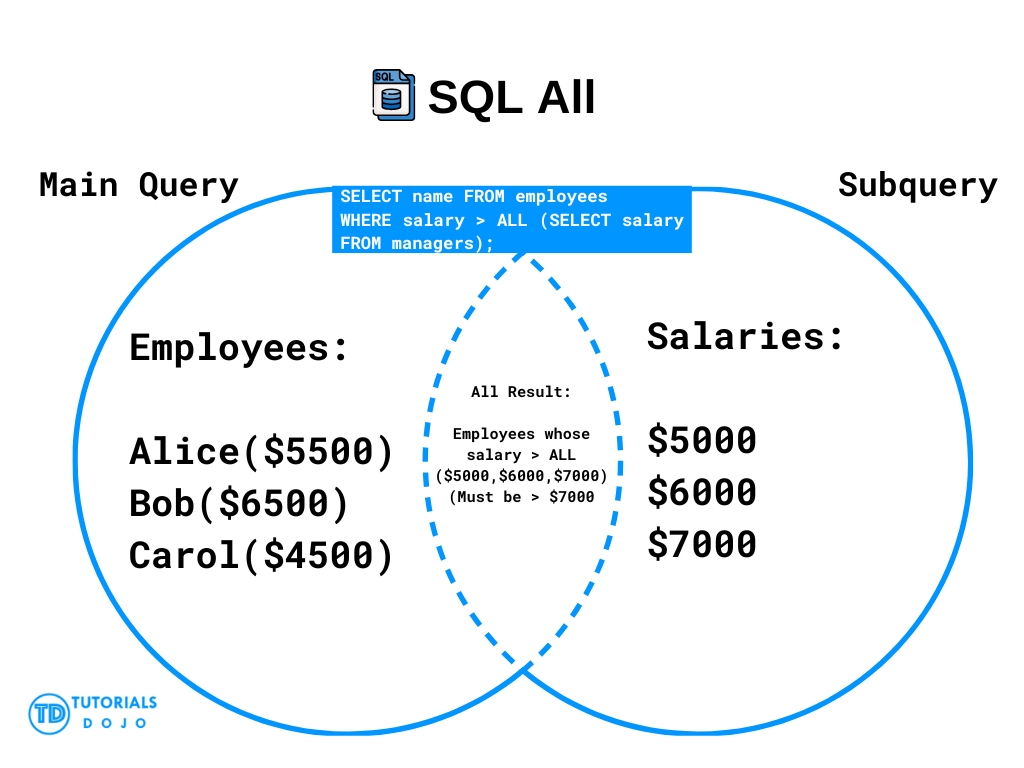
SQL All Doctors with All Appointments After a Certain Date Example
This query checks if all appointments for a doctor occur after the given date. The subquery retrieves doctor_id with future appointments, and the ALL operator ensures that all appointments for each doctor are after that date.
SELECT d.first_name, d.last_name FROM Doctors d WHERE d.doctor_id = ALL ( SELECT a.doctor_id FROM Appointments a WHERE a.appointment_date > '2024-01-01' );
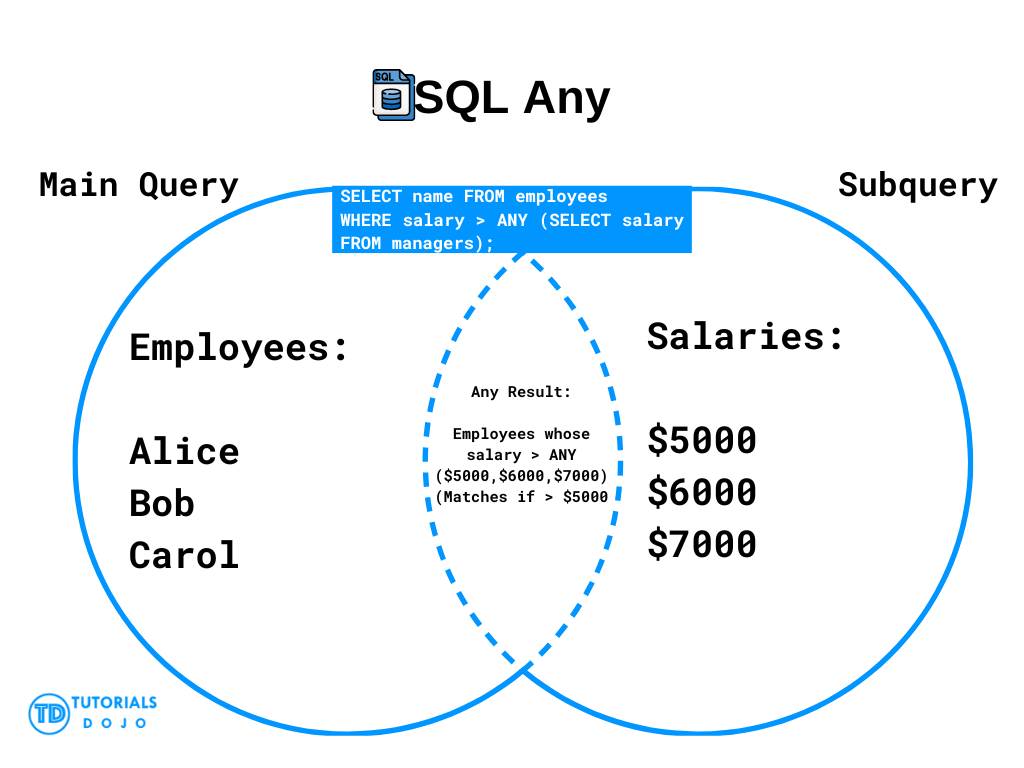
SQL Any Visual Diagram
SQL All Visual Diagram