SQL CASE Keyword
The CASE keyword in SQL is used to create conditional logic in a query. It allows you to return different values based on specific conditions — similar to an IF-THEN-ELSE statement.
SQL CASE Syntax
SELECT column1,
CASE
WHEN condition1 THEN result1
WHEN condition2 THEN result2
...
ELSE result_default
END AS alias_name
FROM table_name;You can also use CASE inside an ORDER BY clause:
SELECT column1, column2
FROM table_name
ORDER BY
CASE
WHEN condition THEN sort_column1
ELSE sort_column2
END;SQL CASE Example with Appointments Table
The following SQL statement shows the appointment ID, status, and a label that changes depending on the value of the status column. This query returns all appointment records and adds a new column status_label based on the value of status.
SELECT appointment_id, status,
CASE
WHEN status = 'Confirmed' THEN 'Confirmed'
WHEN status = 'Scheduled' THEN 'Waiting'
ELSE 'Unknown Status'
END AS status_label
FROM Appointments;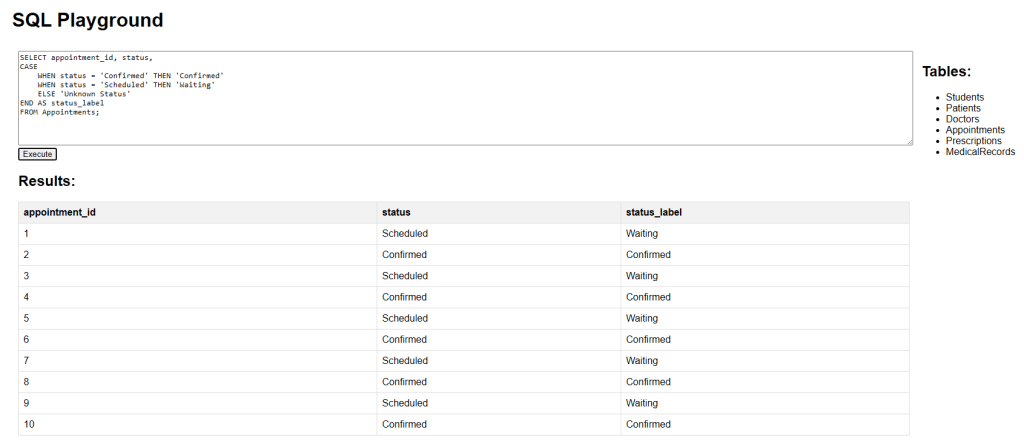
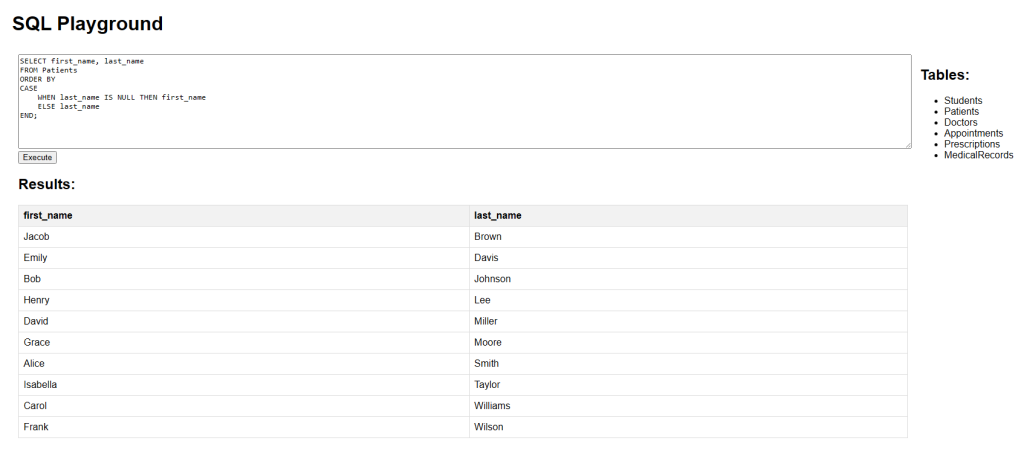
SQL CASE Example in ORDER BY Clause (Patients Table)
This example orders the patients by last_name, but if last_name is NULL, it will order by first_name instead. This ensures that even rows with missing last names are properly sorted using first names.
SELECT first_name, last_name
FROM Patients
ORDER BY
CASE
WHEN last_name IS NULL THEN first_name
ELSE last_name
END;