SQL AS Keyword
The AS keyword in SQL is used to rename a column or a table with an alias. An alias is a temporary name that only exists during the execution of the query. Aliases are useful for making result sets easier to read or for simplifying complex queries.
SQL AS Syntax
For columns:
SELECT column_name AS alias_name FROM table_name;
For tables:
SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name AS alias_name;
SQL AS for Columns
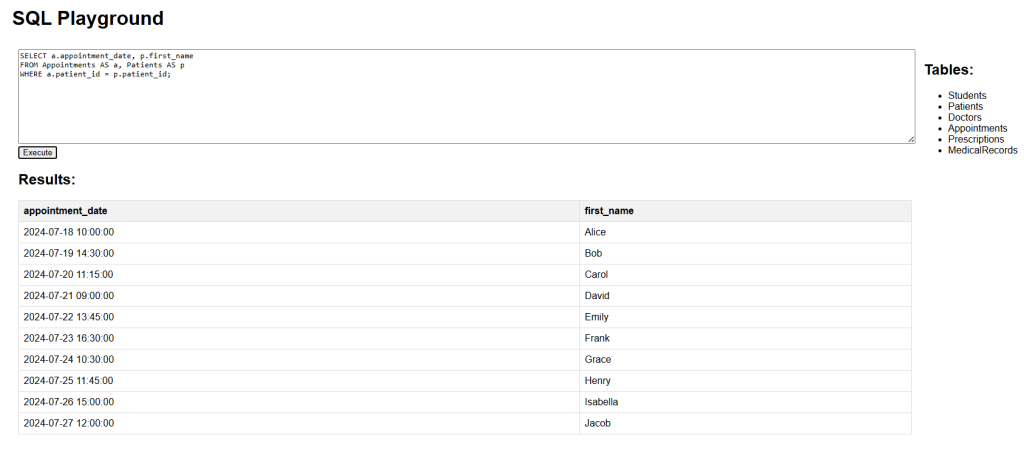
The following SQL statement creates two aliases, one for the first_name column and one for the last_name column from the Patients table:
SELECT first_name AS First, last_name AS Last FROM Patients;
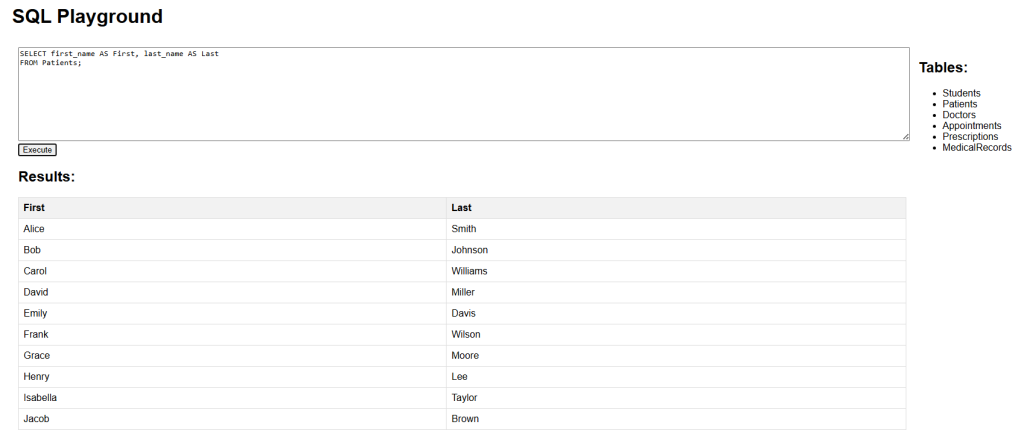
The following SQL statement creates two aliases. Notice that it uses double quotes since the alias contains a space:
SELECT first_name AS "First Name", last_name AS "Last Name" FROM Patients;
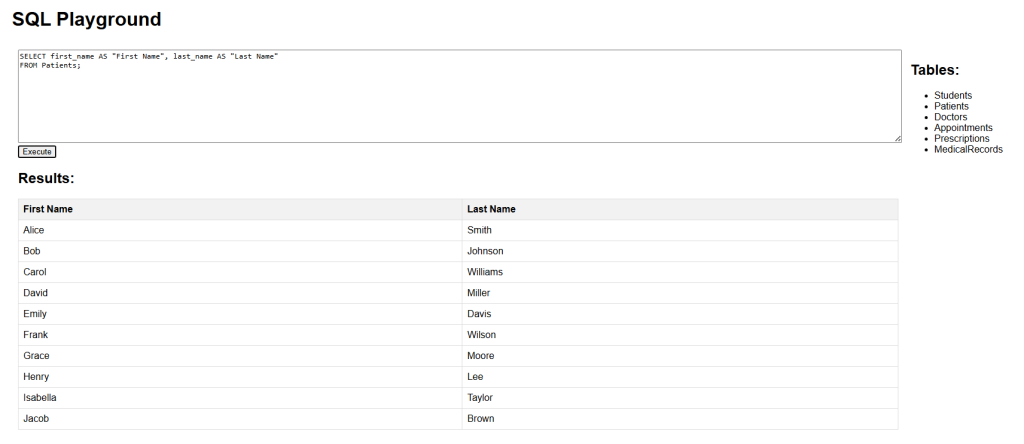
The following SQL statement creates an alias named Details that combines three columns (first_name, last_name, and gender):
SELECT first_name || ' ' || last_name || ' - ' || gender AS Details FROM Patients;
Note: In SQLite (used in our playground),
||is used to concatenate text values.
SQL AS for Tables
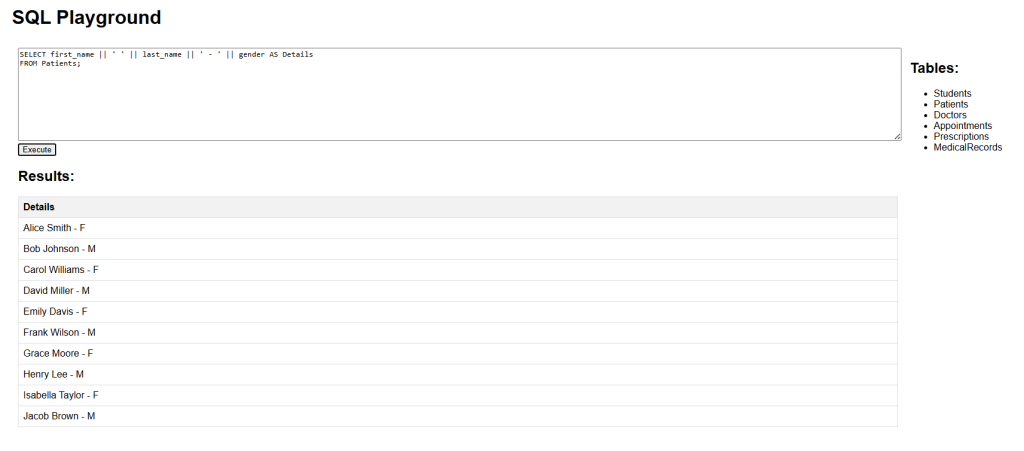
The following SQL statement selects the appointment_date and first_name using aliases for both the Appointments and Patients tables:
SELECT a.appointment_date, p.first_name FROM Appointments AS a, Patients AS p WHERE a.patient_id = p.patient_id;