The GROUP BY statement groups rows with common values into summary rows. It is typically used with aggregate functions like COUNT(), SUM(), AVG(), MIN(), and MAX().
SQL Group By Syntax
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name WHERE condition GROUP BY column_name(s) ORDER BY column_name(s);
SQL Group By Example
Count patients by gender:
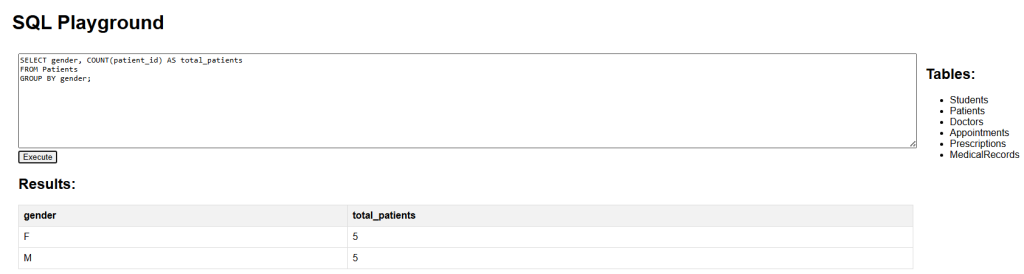
Using the Patients table, we can count how many patients belong to each gender.
SELECT gender, COUNT(patient_id) AS total_patients FROM Patients GROUP BY gender;
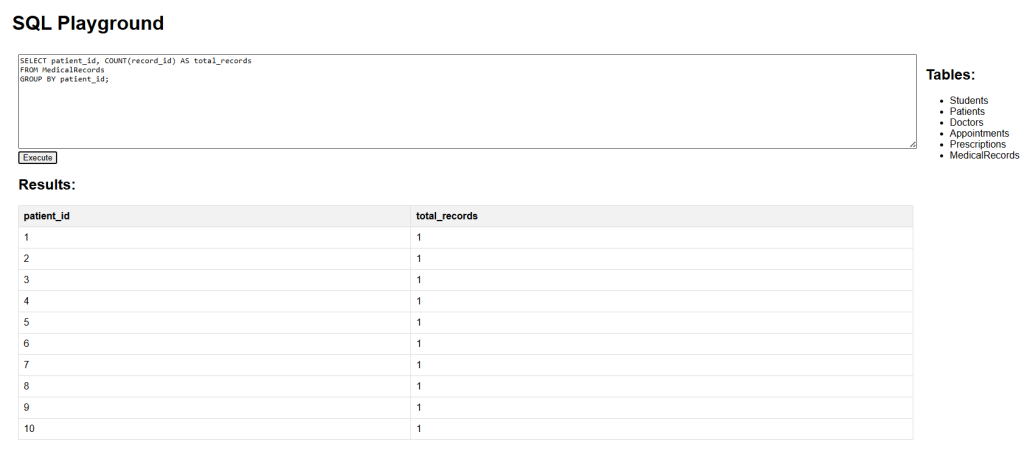
Count medical records per patient:
This retrieves the number of medical records associated with each patient.
SELECT patient_id, COUNT(record_id) AS total_records FROM MedicalRecords GROUP BY patient_id;
SQL GROUP BY with JOIN Example
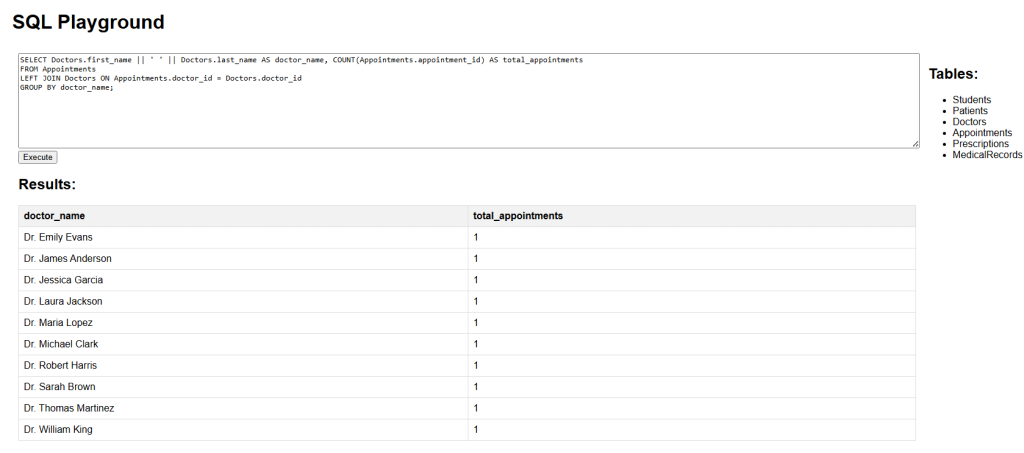
Count appointments per doctor:
To analyze appointment counts for each doctor, we join the Appointments and Doctors tables:
SELECT Doctors.first_name || ' ' || Doctors.last_name AS doctor_name, COUNT(Appointments.appointment_id) AS total_appointments FROM Appointments LEFT JOIN Doctors ON Appointments.doctor_id = Doctors.doctor_id GROUP BY doctor_name;
SQL Group By Visual Diagram