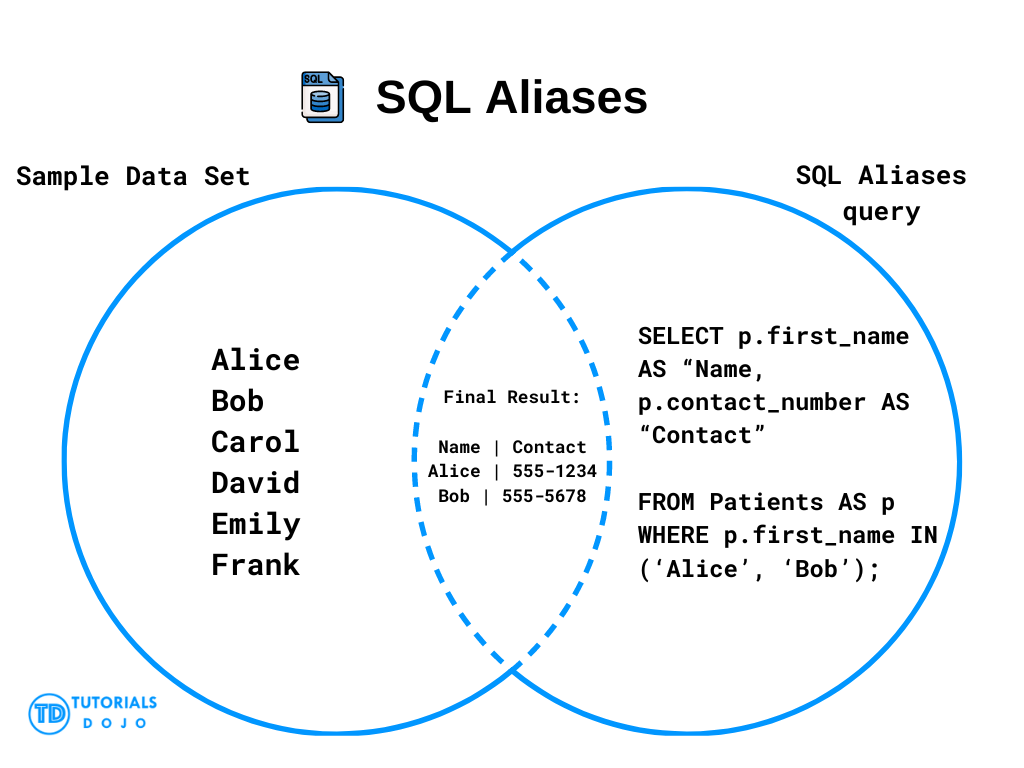
SQL Aliases are temporary names assigned to tables or columns for the duration of a query. They are used to simplify complex queries, improve readability, and provide clarity when dealing with multiple tables or when the original names are lengthy.
SQL Aliases Syntax
SELECT column_name AS alias_name FROM table_name AS alias_name;
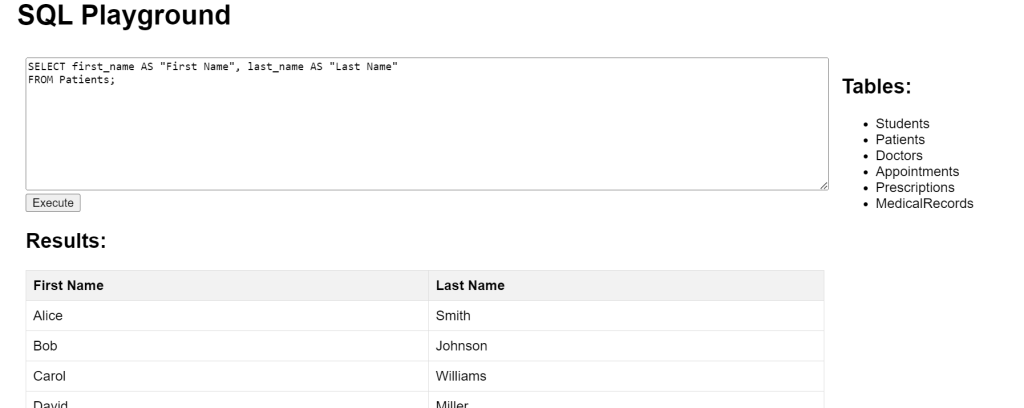
SQL Aliases Basic Example
This query selects the first_name and last_name columns from the Patients table and assigns user-friendly aliases “First Name” and “Last Name” for clearer output.
SELECT first_name AS "First Name", last_name AS "Last Name" FROM Patients;
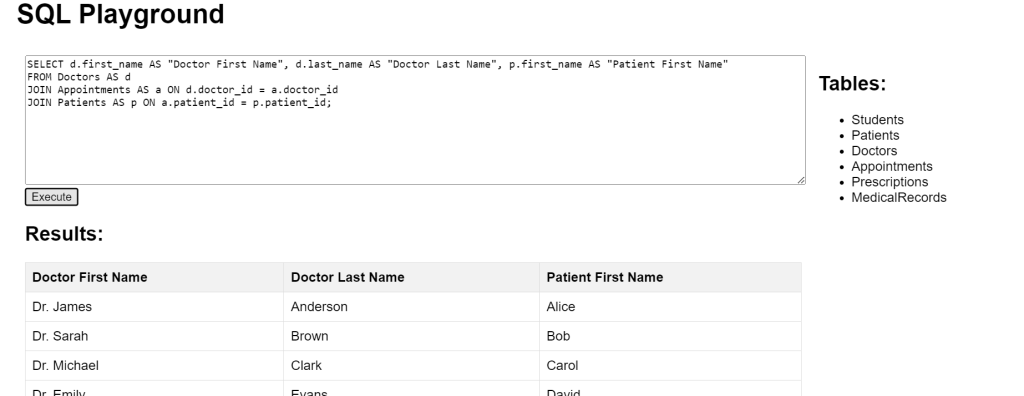
SQL Aliases Alias for Columns Example
In this query, table aliases (d for Doctors, a for Appointments, p for Patients) streamline the selection of doctors and patients names while improving clarity in the output with descriptive aliases.
SELECT d.first_name AS "Doctor First Name", d.last_name AS "Doctor Last Name", p.first_name AS "Patient First Name" FROM Doctors AS d JOIN Appointments AS a ON d.doctor_id = a.doctor_id JOIN Patients AS p ON a.patient_id = p.patient_id;
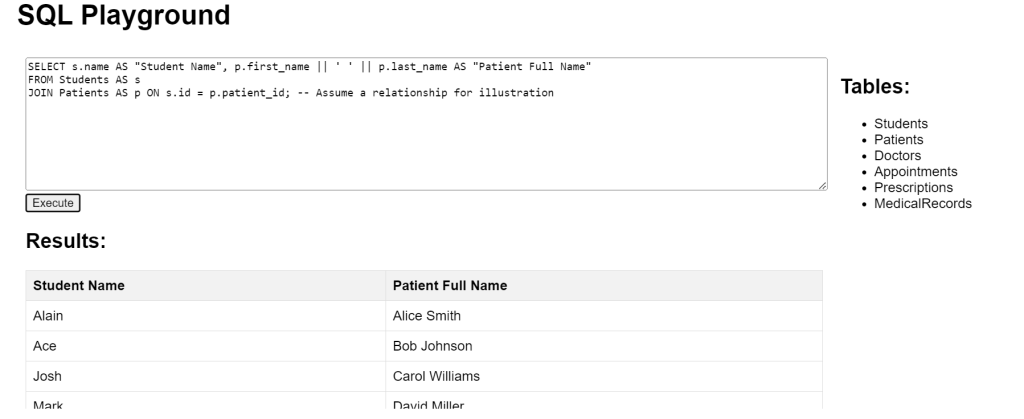
SQL Aliases Combining Aliases Example
This query combines data from Students and Patients using aliases to provide a clear output of “Student Name” and a concatenated “Patient Full Name” while illustrating their assumed relationship.
SELECT s.name AS "Student Name", p.first_name || ' ' || p.last_name AS "Patient Full Name" FROM Students AS s JOIN Patients AS p ON s.id = p.patient_id; -- Assume a relationship for illustration
SQL Aliases Visual Diagram