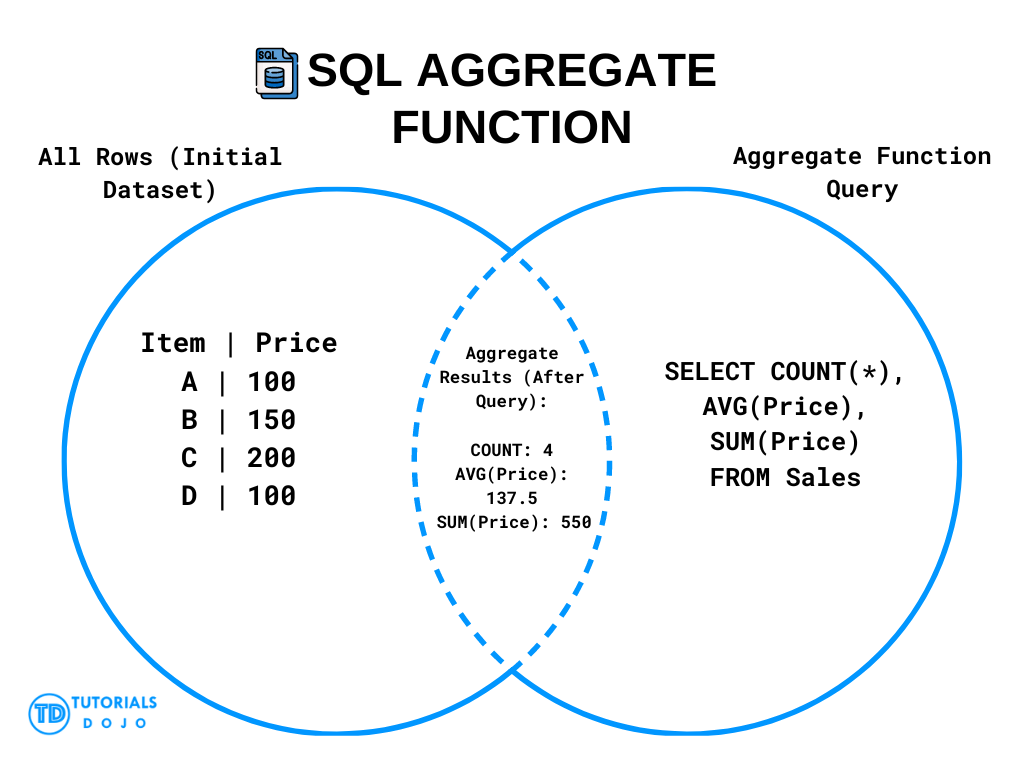
SQL Aggregate Functions perform calculations on a set of values and return a single result. They are used to summarize data and provide insights.
SQL Aggregate Functions Syntax
SELECT AGGREGATE_FUNCTION(column_name) FROM table_name WHERE condition;
SQL Aggregate Functions Example
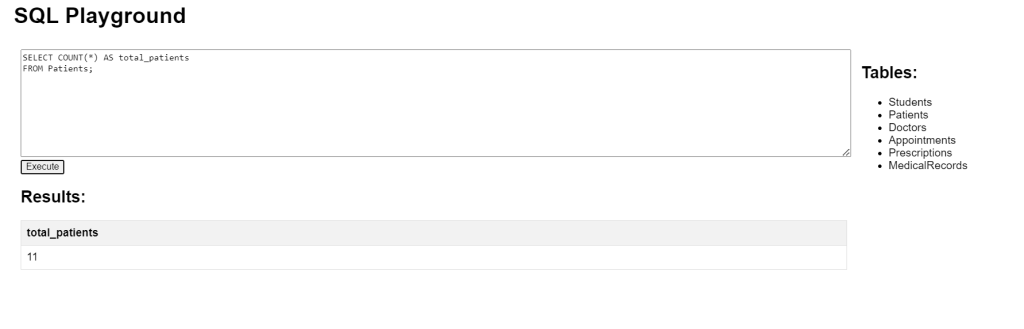
SQL Aggregate Functions COUNT Example
This query counts the total number of rows in the Patients table, giving the total number of patients.
SELECT COUNT(*) AS total_patients FROM Patients;
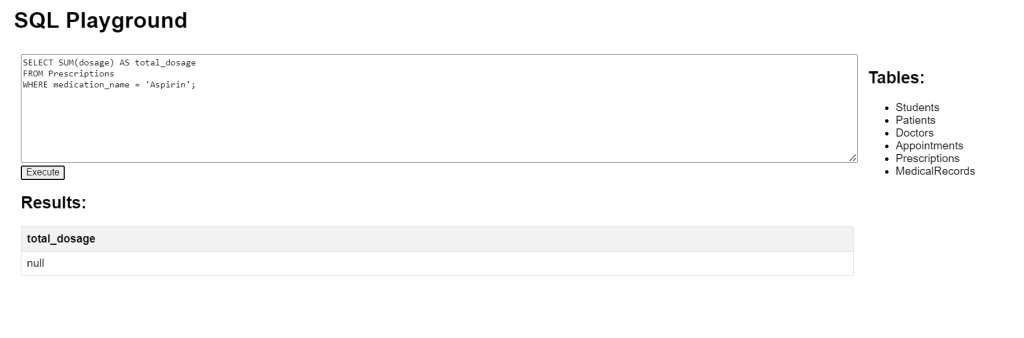
SQL Aggregate Functions SUM Example
This query calculates the total dosage of ‘Aspirin’ from the Prescriptions table. It adds up all values in the dosage column where the medication name is ‘Aspirin’.
SELECT SUM(dosage) AS total_dosage FROM Prescriptions WHERE medication_name = 'Aspirin';
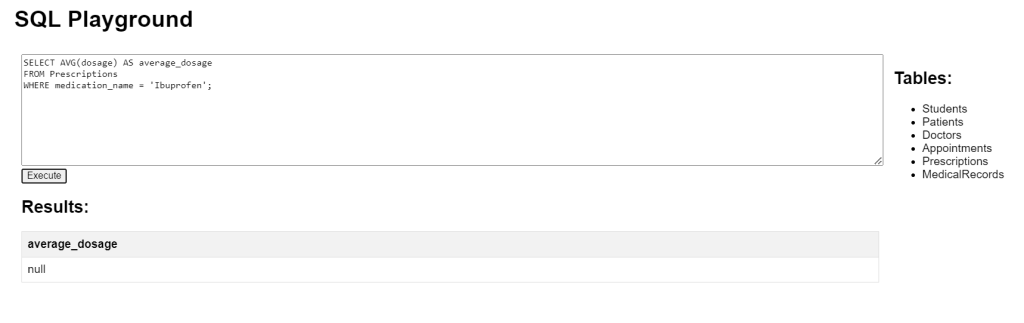
SQL Aggregate Functions AVG Example
This query computes the average dosage of ‘Ibuprofen’ from the Prescriptions table. It finds the average value of the dosage column for rows where the medication name is ‘Ibuprofen’.
SELECT AVG(dosage) AS average_dosage FROM Prescriptions WHERE medication_name = 'Ibuprofen';
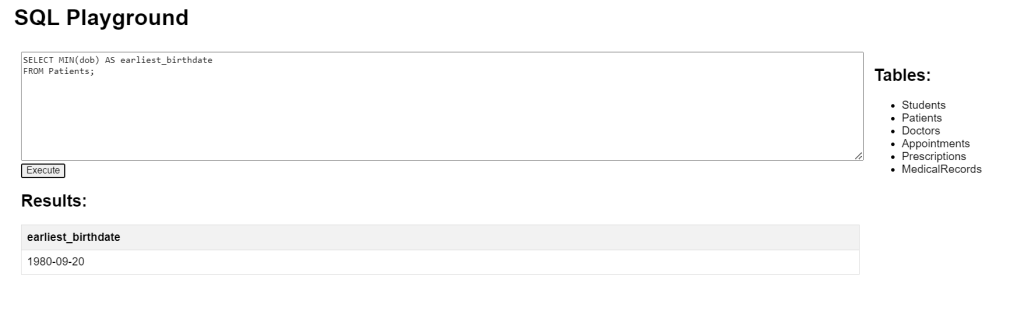
SQL Aggregate Functions MIN Example
This query retrieves the earliest birthdate from the Patients table. The MIN function finds the smallest value in the dob column.
SELECT MIN(dob) AS earliest_birthdate FROM Patients;
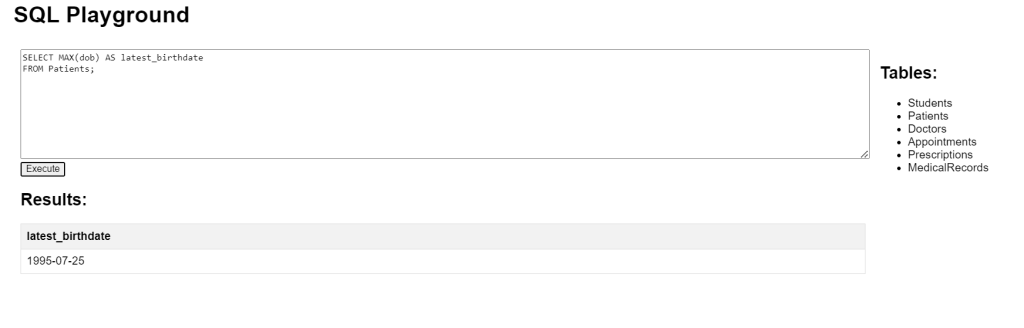
SQL Aggregate Functions MAX Example
This query finds the latest birthdate from the Patients table. The MAX function returns the largest value in the dob (date of birth) column.
SELECT MAX(dob) AS latest_birthdate FROM Patients;
SQL Aggregate Functions Visual Diagram