Dictionaries are unordered collections of key-value pairs. They are useful for storing data that is associated with unique keys, allowing for fast and efficient lookups.
Creating Dictionaries
You can create a dictionary by placing key-value pairs inside curly braces {}, separated by commas. Each key is followed by a colon and its associated value.
Dictionaries allow you to store and retrieve values using unique keys. Keys can be of immutable types such as strings and numbers, while values can be of any data type.
# Creating a dictionarystudent = { "name": "Alice", "age": 21, "courses": ["Math", "Computer Science"]}Accessing Dictionary Items
You can access items in a dictionary by using their keys.
Use the key inside square brackets to get the corresponding value from the dictionary.
# Accessing dictionary itemsprint(student["name"]) # Output: Aliceprint(student["courses"]) # Output: ['Math', 'Computer Science']Modifying Dictionary Items
Dictionaries are mutable, meaning you can change their items after creation.
You can modify the value associated with a key by assigning a new value to that key.
# Modifying dictionary itemsstudent["age"] = 22student["courses"].append("Physics")print(student) # Output: {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 22, 'courses': ['Math', 'Computer Science', 'Physics']}Adding and Removing Items
You can add new key-value pairs to a dictionary and remove existing ones.
- To add a new item, assign a value to a new key.
- To remove an item, use the
delstatement or thepop()method.
# Adding items to a dictionarystudent["grade"] = "A"print(student) # Output: {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 22, 'courses': ['Math', 'Computer Science', 'Physics'], 'grade': 'A'}# Removing items from a dictionarydel student["age"]grade = student.pop("grade")print(student) # Output: {'name': 'Alice', 'courses': ['Math', 'Computer Science', 'Physics']}print(grade) # Output: ADictionary Methods
Python provides several built-in methods for dictionary manipulation.
- keys(): Returns a list of keys in the dictionary.
- values(): Returns a list of values in the dictionary.
- items(): Returns a list of key-value pairs in the dictionary.
- get(): Returns the value for a key, or a default value if the key is not found.
# Dictionary methodskeys = student.keys()values = student.values()items = student.items()age = student.get("age", "N/A")print("Keys:", keys) # Output: Keys: dict_keys(['name', 'courses'])print("Values:", values) # Output: Values: dict_values(['Alice', ['Math', 'Computer Science', 'Physics']])print("Items:", items) # Output: Items: dict_items([('name', 'Alice'), ('courses', ['Math', 'Computer Science', 'Physics'])])print("Age:", age) # Output: Age: N/APython Dictionaries Example Code
This program creates a dictionary of student information and demonstrates accessing, modifying, adding, removing items, and using dictionary methods.
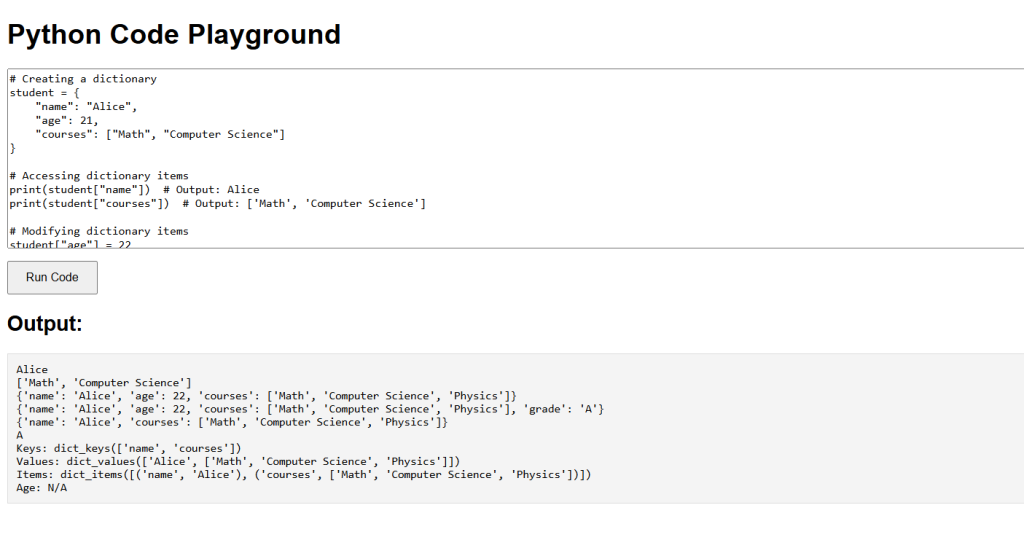
# Creating a dictionarystudent = { "name": "Alice", "age": 21, "courses": ["Math", "Computer Science"]}# Accessing dictionary itemsprint(student["name"]) # Output: Aliceprint(student["courses"]) # Output: ['Math', 'Computer Science']# Modifying dictionary itemsstudent["age"] = 22student["courses"].append("Physics")print(student) # Output: {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 22, 'courses': ['Math', 'Computer Science', 'Physics']}# Adding items to a dictionarystudent["grade"] = "A"print(student) # Output: {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 22, 'courses': ['Math', 'Computer Science', 'Physics'], 'grade': 'A'}# Removing items from a dictionarydel student["age"]grade = student.pop("grade")print(student) # Output: {'name': 'Alice', 'courses': ['Math', 'Computer Science', 'Physics']}print(grade) # Output: A# Dictionary methodskeys = student.keys()values = student.values()items = student.items()age = student.get("age", "N/A")print("Keys:", keys) # Output: Keys: dict_keys(['name', 'courses'])print("Values:", values) # Output: Values: dict_values(['Alice', ['Math', 'Computer Science', 'Physics']])print("Items:", items) # Output: Items: dict_items([('name', 'Alice'), ('courses', ['Math', 'Computer Science', 'Physics'])])print("Age:", age) # Output: Age: N/A