Booleans are a fundamental data type in Python that can hold one of two values: True or False. Booleans are commonly used in conditional statements and loops to control the flow of a program.
Boolean Values
In Python, Boolean values are represented by the keywords True and False.
- True represents a logical high or affirmative value.
- False represents a logical low or negative value.
is_active = True is_student = False
Boolean Expressions
Boolean expressions are expressions that evaluate to either True or False. These expressions often involve comparison operators or logical operators.
- Comparison Operators:
These operators compare two values and return a Boolean value.
x = 5 y = 10 print(x == y) # Output: False print(x < y) # Output: True
- Logical Operators:
These operators combine Boolean values and return a Boolean result.
a = True b = False print(a and b) # Output: False print(a or b) # Output: True print(not a) # Output: False
Boolean Functions
Python has built-in functions that return Boolean values.
The bool() function can be used to check the truthiness of a value.
- bool() – Converts a value to a Boolean. Most values evaluate to
True, except for empty collections, zero, andNone.
print(bool(1)) # Output: True print(bool(0)) # Output: False print(bool([])) # Output: False print(bool([1, 2])) # Output: True
Using Booleans in Conditional Statements
Booleans are often used in conditional statements to control the flow of a program.
- if Statements:
The if statement evaluates the condition and executes the corresponding block of code based on whether the condition is True or False.
is_raining = True
if is_raining:
print("Take an umbrella.")
else:
print("Enjoy the sunshine!")- while Loops:
The while loop continues to execute the block of code as long as the condition is True.
count = 0
while count < 5:
print("Count:", count)
count += 1Python Boolean Example Code
This program uses Boolean values and expressions in conditional statements and loops to control the flow of execution.
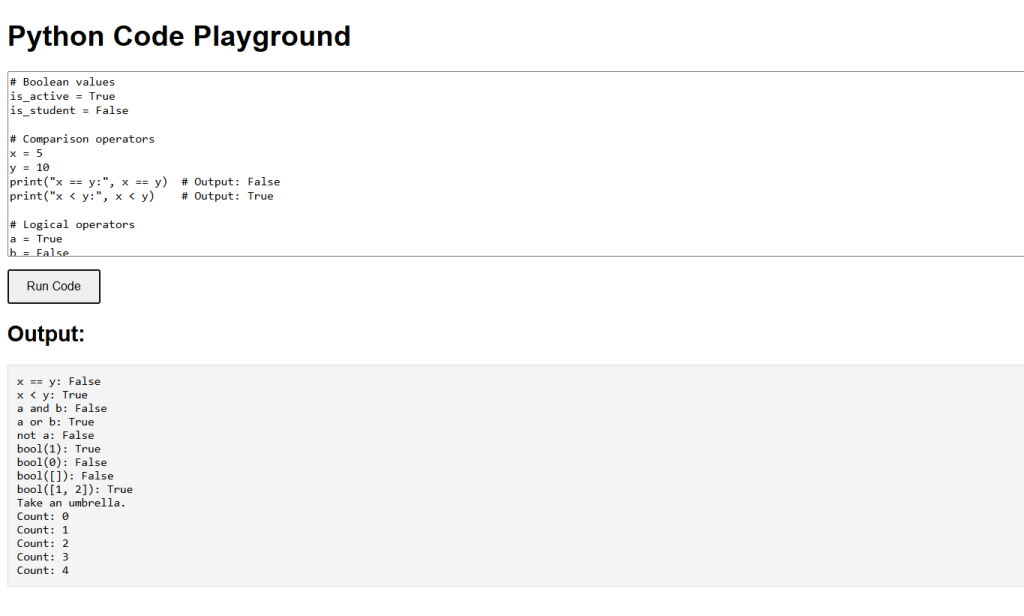
# Boolean values
is_active = True
is_student = False
# Comparison operators
x = 5
y = 10
print("x == y:", x == y) # Output: False
print("x < y:", x < y) # Output: True
# Logical operators
a = True
b = False
print("a and b:", a and b) # Output: False
print("a or b:", a or b) # Output: True
print("not a:", not a) # Output: False
# Boolean function
print("bool(1):", bool(1)) # Output: True
print("bool(0):", bool(0)) # Output: False
print("bool([]):", bool([])) # Output: False
print("bool([1, 2]):", bool([1, 2])) # Output: True
# Using booleans in conditional statements
is_raining = True
if is_raining:
print("Take an umbrella.")
else:
print("Enjoy the sunshine!")
# Using booleans in while loops
count = 0
while count < 5:
print("Count:", count)
count += 1