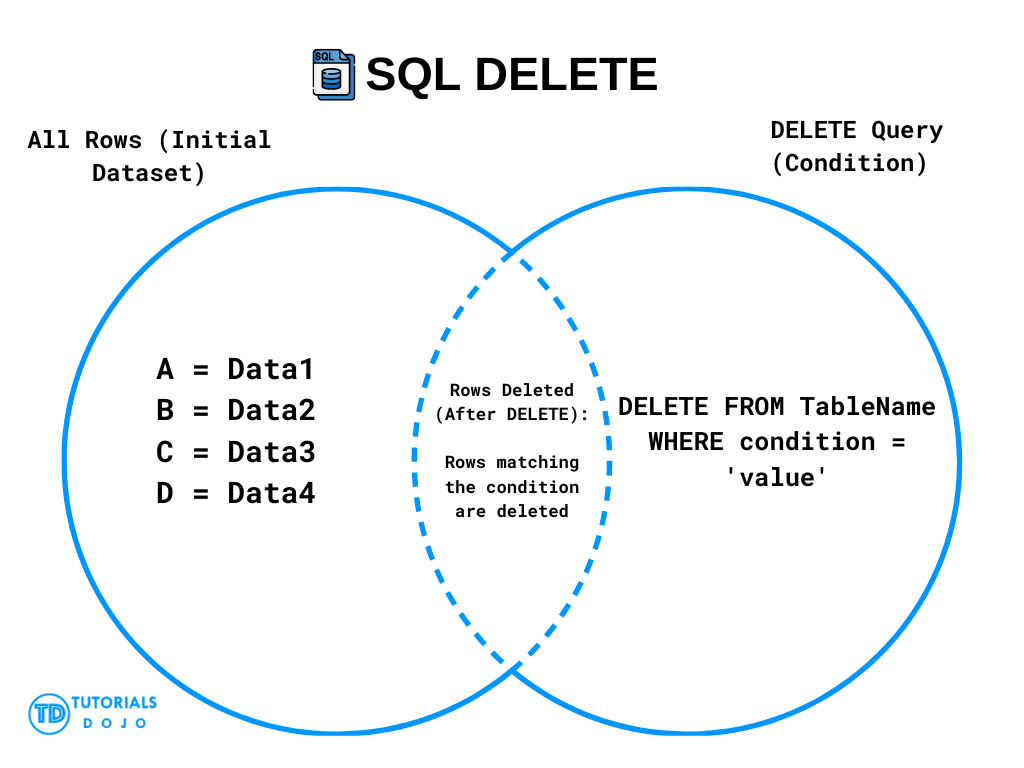
The DELETE in SQL is used to remove existing records from a table. It allows you to delete one or more rows based on specified conditions.
SQL Delete Syntax
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition;
SQL Delete Example
This query deletes the record from the Patients table where the patient_id is 3. This means the entire record for the patient with patient_id = 3 will be removed from the table.
DELETE FROM Patients WHERE patient_id = 3;

SQL Delete All Records Example
This query deletes all records from the Prescriptions table. This means that every entry in the Presciptions table will be removed, leaving the table empty.
DELETE FROM Prescriptions;

SQL Delete Multiple Records Example
This query deletes all records from the Appointments table where the appointment_date is ‘2024-07-18’.
DELETE FROM Appointments WHERE appointment_date = '2024-07-18';

SQL Delete with Complex Conditions Example
This query deletes all records from the Patients table where the dob (date of birth) is earlier than ‘1980-01-01’.
DELETE FROM Patients WHERE dob < '1980-01-01';

SQL Delete with Subqueries Example
This query deletes all records from the Doctors table where the doctor_id is not present in the Appointments table. This means that any doctor who does not have any scheduled appointments will be removed from the Doctors table.
DELETE FROM Doctors
WHERE doctor_id NOT IN (
SELECT doctor_id FROM Appointments
);
SQL Delete Visual Diagram