Creating a Date Object
The Date object is used to work with dates and times. You can create a new Date object using the Date constructor.
Explanation of Code:
This example creates a Date object representing the current date and time.
let currentDate = new Date(); console.log(currentDate); // Output: Current date and time
Getting Date and Time Values
This example demonstrates how to get various parts of the date and time using methods like getFullYear(), getMonth(), getDate(), getHours(), getMinutes(), getSeconds(), getMilliseconds(), and getDay().
let date = new Date();
let year = date.getFullYear();
console.log("Year: " + year); // Output: Year: current year
let month = date.getMonth() + 1;
console.log("Month: " + month); // Output: Month: current month (0-11, so add 1)
let day = date.getDate();
console.log("Day: " + day); // Output: Day: current day of the month
let hours = date.getHours();
console.log("Hours: " + hours); // Output: Hours: current hour (0-23)
let minutes = date.getMinutes();
console.log("Minutes: " + minutes); // Output: Minutes: current minute (0-59)
let seconds = date.getSeconds();
console.log("Seconds: " + seconds); // Output: Seconds: current second (0-59)
let milliseconds = date.getMilliseconds();
console.log("Milliseconds: " + milliseconds); // Output: Milliseconds: current millisecond (0-999)
let dayOfWeek = date.getDay();
console.log("Day of the Week: " + dayOfWeek); // Output: Day of the Week: current day (0-6, Sunday=0)Setting Date and Time Values
This example demonstrates how to set various parts of the date and time using methods like setFullYear(), setMonth(), setDate(), setHours(), setMinutes(), setSeconds(), and setMilliseconds().
let date = new Date();
date.setFullYear(2025);
console.log("Year: " + date.getFullYear()); // Output: Year: 2025
date.setMonth(11); // December (0-11)
console.log("Month: " + (date.getMonth() + 1)); // Output: Month: 12
date.setDate(25);
console.log("Day: " + date.getDate()); // Output: Day: 25
date.setHours(10);
console.log("Hours: " + date.getHours()); // Output: Hours: 10
date.setMinutes(30);
console.log("Minutes: " + date.getMinutes()); // Output: Minutes: 30
date.setSeconds(45);
console.log("Seconds: " + date.getSeconds()); // Output: Seconds: 45
date.setMilliseconds(500);
console.log("Milliseconds: " + date.getMilliseconds()); // Output: Milliseconds: 500Parsing Dates
You can create Date objects from date strings using the Date.parse() method or the Date constructor.
Explanation of Code:
The Date.parse() method parses a date string and returns the number of milliseconds since January 1, 1970, which can be used to create a Date object.
let dateString = "2024-11-11T12:00:00Z"; let parsedDate = new Date(Date.parse(dateString)); console.log(parsedDate); // Output: Parsed date and time
Formatting Dates
You can format dates using various methods like toDateString(), toTimeString(), toLocaleDateString(), toLocaleTimeString(), etc.
Explanation of Code:
This example demonstrates how to format dates using methods like toDateString(), toTimeString(), toLocaleDateString(), and toLocaleTimeString().
let date = new Date();
console.log("Date String: " + date.toDateString()); // Output: Date String: current date in readable format
console.log("Time String: " + date.toTimeString()); // Output: Time String: current time in readable format
console.log("Locale Date String: " + date.toLocaleDateString()); // Output: Locale Date String: current date in localized format
console.log("Locale Time String: " + date.toLocaleTimeString()); // Output: Locale Time String: current time in localized formatJavaScript Date and Time Example Code
Explanation of Code:
- Creating a Date Object: Creates a
Dateobject with the current date and time. - Getting Date Components: Retrieves various components of the date and time.
- Setting Date Components: Updates various components of the date and time.
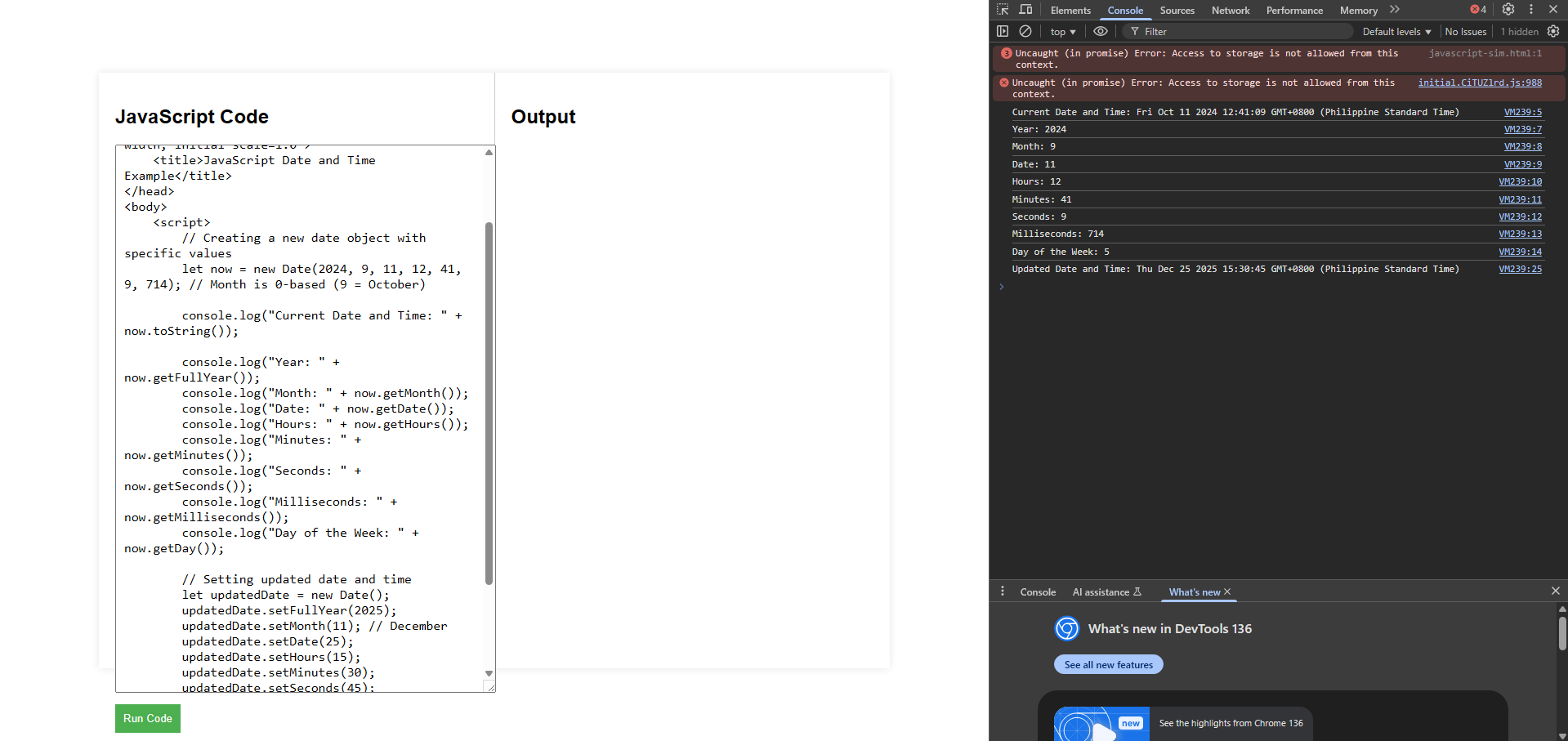
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>JavaScript Date and Time Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// Creating a new date object with specific values
let now = new Date(2024, 9, 11, 12, 41, 9, 714); // Month is 0-based (9 = October)
console.log("Current Date and Time: " + now.toString());
console.log("Year: " + now.getFullYear());
console.log("Month: " + now.getMonth());
console.log("Date: " + now.getDate());
console.log("Hours: " + now.getHours());
console.log("Minutes: " + now.getMinutes());
console.log("Seconds: " + now.getSeconds());
console.log("Milliseconds: " + now.getMilliseconds());
console.log("Day of the Week: " + now.getDay());
// Setting updated date and time
let updatedDate = new Date();
updatedDate.setFullYear(2025);
updatedDate.setMonth(11); // December
updatedDate.setDate(25);
updatedDate.setHours(15);
updatedDate.setMinutes(30);
updatedDate.setSeconds(45);
console.log("Updated Date and Time: " + updatedDate.toString());
</script>
</body>
</html>