What is a Function?
A function is a block of code designed to perform a particular task. Functions are executed when they are called (invoked). This allows you to reuse code, making your programs more modular and easier to maintain.
Defining a Function
To define a function in JavaScript, you use the function keyword followed by a name, parentheses () which may include parameters, and a block of code {}.
Explanation of Code:
This example defines a function named greet that logs “Hello, World!” to the console when called.
function greet() {
console.log("Hello, World!");
}Calling a Function
To execute the code inside a function, you need to call it by its name followed by parentheses ().
Explanation of Code:
This calls the greet function, which logs the message to the console.
greet(); // Output: Hello, World!
Function Paramaters
Functions can accept parameters, which are values passed to the function when it is called. You can use these parameters within the function.
Explanation of Code:
The greet function now accepts a name parameter, which is used to customize the greeting message.
function greet(name) {
console.log("Hello, " + name + "!");
}
greet("Alice"); // Output: Hello, Alice!Function Return Values
Functions can return a value using the return statement. The returned value can be used in the code that called the function.
Explanation of Code:
The add function takes two parameters, a and b, and returns their sum. The result is stored in the sum variable and then logged to the console.
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
let sum = add(5, 3);
console.log(sum); // Output: 8Anonymous Functions
Functions can also be defined without a name, known as anonymous functions. These are often used as arguments to other functions or assigned to variables.
Explanation of Code:
An anonymous function is assigned to the variable greet, and it works similarly to a named function.
let greet = function(name) {
console.log("Hello, " + name + "!");
};
greet("Bob"); // Output: Hello, Bob!Arrow Functions
Arrow functions provide a more concise syntax for writing functions. They are particularly useful for writing short, anonymous functions.
Explanation of Code:
The arrow function syntax => is used to define the function, making it more concise.
let greet = (name) => {
console.log("Hello, " + name + "!");
};
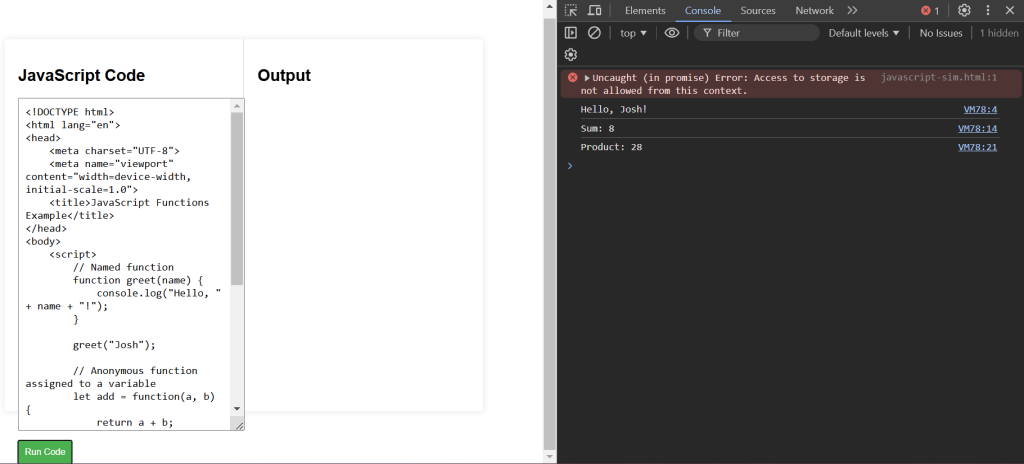
greet("Charlie"); // Output: Hello, Charlie!JavaScript Functions Example Code
Explanation of Code:
- Named Function: Defines and calls a function named
greet. - Anonymous Function: Defines an anonymous function and assigns it to the variable
add. - Arrow Function: Defines a function using arrow function syntax and assigns it to the variable
multiply.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>JavaScript Functions Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// Named function
function greet(name) {
console.log("Hello, " + name + "!");
}
greet("Josh");
// Anonymous function assigned to a variable
let add = function(a, b) {
return a + b;
};
console.log("Sum: " + add(5, 3));
// Arrow function
let multiply = (a, b) => {
return a * b;
};
console.log("Product: " + multiply(4, 7));
</script>
</body>
</html>