Primitive Data Types
JavaScript has several primitive data types that represent simple values.
1. Number
The number data type represents both integer and floating-point numbers.
let age = 25; // Integer let price = 19.99; // Floating-point console.log(typeof age); // Output: "number" console.log(typeof price); // Output: "number"
2. String
The string data type is used to represent text. Strings are enclosed in single quotes ('), double quotes ("), or backticks (`).
let name = "John";
let greeting = 'Hello, World!';
let template = `My name is ${name}`;
console.log(typeof name); // Output: "string"
console.log(typeof greeting); // Output: "string"
console.log(template); // Output: "My name is John"3. Boolean
The boolean data type represents a logical value: true or false.
let isJavaScriptFun = true; let isItRaining = false; console.log(typeof isJavaScriptFun); // Output: "boolean" console.log(typeof isItRaining); // Output: "boolean"
4. Undefined
A variable that has been declared but not assigned a value is of type undefined.
let uninitialized; console.log(typeof uninitialized); // Output: "undefined"
5. Null
The null data type represents an intentional absence of any object value. It is treated as an object type, but this is actually a bug in JavaScript.
let emptyValue = null; console.log(typeof emptyValue); // Output: "object"
6. Symbol
The symbol data type is used to create unique identifiers for objects.
let uniqueId = Symbol("id");
console.log(typeof uniqueId); // Output: "symbol"Complex Data Type
JavaScript also has a complex data type known as Object.
Object
Objects are collections of key-value pairs. They can store multiple values as properties.
let person = {
firstName: "John",
lastName: "Doe",
age: 30,
isEmployed: true
};
console.log(typeof person); // Output: "object"
console.log(person.firstName); // Output: "John"JavaScript Data Types Example Code
Explanation of Code:
- Number: Declares a variable
agewith a numeric value. - String: Declares a variable
namewith a string value. - Boolean: Declares a variable
isStudentwith a boolean value. - Undefined: Declares a variable
citywithout assigning a value. - Null: Declares a variable
carwith a null value. - Symbol: Declares a variable
symwith a unique symbol. - Object: Declares a variable
personwith properties.
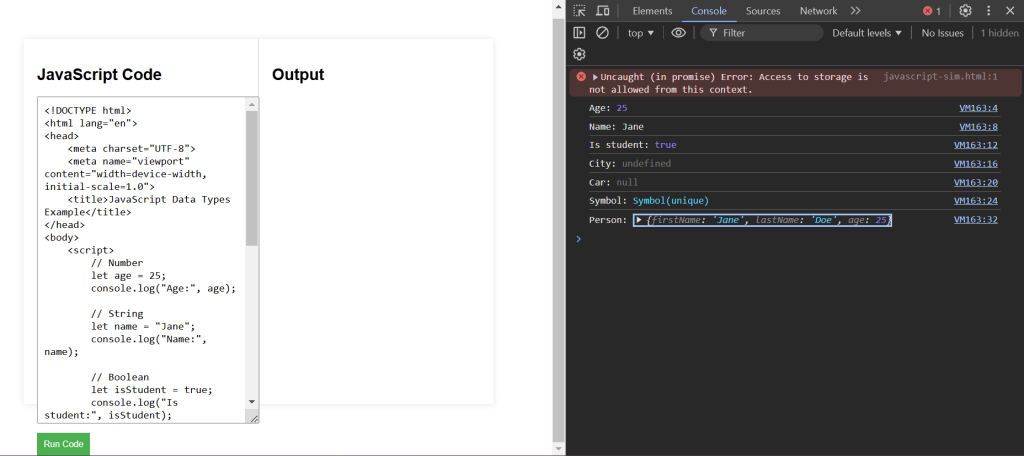
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>JavaScript Data Types Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// Number
let age = 25;
console.log("Age:", age);
// String
let name = "Jane";
console.log("Name:", name);
// Boolean
let isStudent = true;
console.log("Is student:", isStudent);
// Undefined
let city;
console.log("City:", city);
// Null
let car = null;
console.log("Car:", car);
// Symbol
let sym = Symbol("unique");
console.log("Symbol:", sym);
// Object
let person = {
firstName: "Jane",
lastName: "Doe",
age: 25
};
console.log("Person:", person);
</script>
</body>
</html>