In this lesson, we will explore ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) roles and how they enhance user experience by improving accessibility for individuals with disabilities. We will discuss the purpose of ARIA roles, common roles used in HTML, and best practices for implementation.
What are ARIA Roles?
ARIA roles provide additional semantic information to assistive technologies, helping users understand the purpose of web elements. They are particularly useful in complex web applications where native HTML elements may not convey the necessary meaning.
Common ARIA Roles
role="navigation": Indicates a navigation section of the page.
<nav role="navigation">
<ul>
<li><a href="#home">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="#about">About</a></li>
<li><a href="#contact">Contact</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>role="main": Identifies the primary content of the document.
<main role="main">
<h1>Welcome to Our Website</h1>
<p>This is the main content area.</p>
</main>role="banner": Represents the header of the page.
<header role="banner">
<h1>My Website</h1>
</header>role="complementary": Defines content that complements the main content.
<aside role="complementary">
<h2>Related Articles</h2>
<ul>
<li><a href="#article1">Article 1</a></li>
<li><a href="#article2">Article 2</a></li>
</ul>
</aside>role="dialog": Marks a dialog or modal window.
<div role="dialog" aria-labelledby="dialogTitle">
<h2 id="dialogTitle">Dialog Title</h2>
<p>This is a dialog window.</p>
<button>Close</button>
</div>Implementing ARIA Roles
To implement ARIA roles effectively:
- Identify the Purpose: Understand the role of each element in your application and assign the appropriate ARIA role.
- Use Additional ARIA Attributes: Utilize attributes like
aria-label,aria-hidden, andaria-expandedfor added context. - Test Accessibility: Use screen readers to ensure proper interpretation of roles and to enhance user experience.
HTML Enhancing User Experience with ARIA Roles Example Code
Explanation of Code:
- The
<header>usesrole="banner"to denote the header of the page. - The
<nav>element specifiesrole="navigation"for the navigation links. - The
<main>tag is marked withrole="main"to indicate the primary content area. - The
<aside>section usesrole="complementary"for supplementary content. - The
<footer>employsrole="contentinfo"for the footer information.
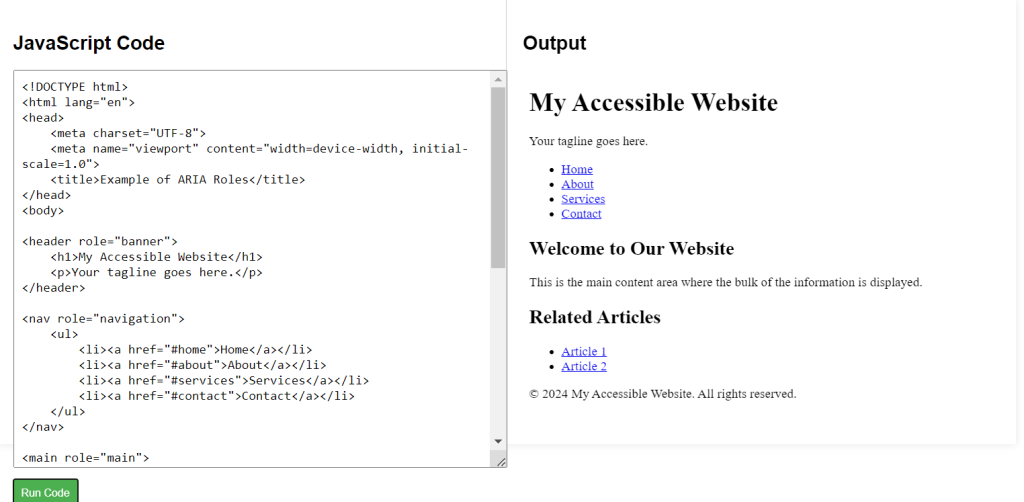
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Example of ARIA Roles</title>
</head>
<body>
<header role="banner">
<h1>My Accessible Website</h1>
<p>Your tagline goes here.</p>
</header>
<nav role="navigation">
<ul>
<li><a href="#home">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="#about">About</a></li>
<li><a href="#services">Services</a></li>
<li><a href="#contact">Contact</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
<main role="main">
<section>
<h2>Welcome to Our Website</h2>
<p>This is the main content area where the bulk of the information is displayed.</p>
</section>
<aside role="complementary">
<h2>Related Articles</h2>
<ul>
<li><a href="#article1">Article 1</a></li>
<li><a href="#article2">Article 2</a></li>
</ul>
</aside>
</main>
<footer role="contentinfo">
<p>© 2024 My Accessible Website. All rights reserved.</p>
</footer>
</body>
</html>